5 Methods to Prepare Molybdenum Carbide
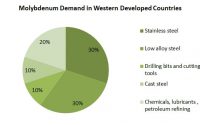
Molybdenum is distributed in very small amounts in the earth’s crust, with an abundance of about 0.0003%. Molybdenum carbide, a compound of molybdenum, has become a hot spot in the research field of new inorganic catalytic materials due to its unique electronic structure and excellent catalytic properties. Molybdenum carbide has strong catalytic activity for hydrocarbon dehydrogenation, hydrocarbon denitrogenation, hydrogenolysis, and isomerization, and is a promising new catalytic material. This article mainly introduces 5 methods for preparing molybdenum carbide.

Temperature-programmed reduction
This method was proposed in the 1980s and is still the mainstream method for preparing molybdenum carbide in the laboratory.
This method was proposed in the 1980s and is still the mainstream method for preparing molybdenum carbide in the laboratory.
Step 1: Molybdenum oxide is used as a molybdenum source, and hydrocarbon gas and hydrogen gas are used as basic materials for carbon dioxide and gas reduction, respectively;
Step 2: Raise the temperature slowly to ensure that the catalytic rate is balanced during the reaction;
Step 3: Monitor the composition and content of the exhaust gas by chromatography, and evaluate the reaction process accordingly, and stop the reaction with the carbonized raw materials in time to obtain molybdenum carbide with a larger surface area.
Sol-gel method
Step 1: Heat the gel and evaporate at 60℃~80℃;
Step 2: Heating in hydrogen at 850°C for 14h to obtain hexagonal MoC.
Step 3: Add an appropriate amount of nickel acetate to obtain nickel and nickel carbide for modifying MoC.
Chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition is a widely used thin film fabrication method. Chemical reactions take place in the gas phase to deposit solids on the surface of the heated solid substrate. Some researchers used a two-step precipitation method and carbon dioxide formation method to obtain MoC thin layers.
Further reading: What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)?
Microwave pyrolysis
The main advantage of microwave pyrolysis is rapid heating, that is, the system temperature can reach the set value in a short time. In this method, the preparation time is greatly reduced, thereby effectively suppressing the hot particle phenomenon. The molybdenum carbide particles obtained from the microwave solution were uniform and small in size.
Biomass Carbonization
In recent years, a method for extracting carbides from biomass has emerged. Biomass refers to various organisms formed through photosynthesis, including all animals, plants and microorganisms. Biomass can be used for the mass production of carbides. Because the carbon dioxide reaction occurs between solid and solid phases, it is easy to control.
For more information, please visit https://www.samaterials.com/.