High Purity Tungsten Powder: Preparation and Applications
Introduction
High purity tungsten powder refers to tungsten powder with a chemical purity of at least 99.99%. This level of purity can range from 99.99% to 99.999%, with impurity elements present at extremely low concentrations, typically between (0.1 ~ 1000)×10^-12. The stringent requirements for high purity tungsten powder extend to specific impurity elements, including radioactive elements, alkali metal elements, heavy metals, and gas elements, ensuring minimal contamination.

Products Made from High Purity Tungsten Powder
High purity tungsten powder is the basis for a variety of high-performance tungsten products, including:
- Tungsten Bar: High-density bars used in aerospace, defense, and industrial applications.
- Tungsten Rod: Versatile rods employed in manufacturing, electronics, and research.
- Tungsten Electrode: Critical components in welding and electronic devices.
- Tungsten Wire: Essential in lighting, electronic devices, and high-temperature applications.
- Tungsten Sheet and Plate: Used in electronics, high-temperature furnaces, and other specialized applications.
- Pure Tungsten: Utilized in precision instruments and high-tech devices.
- Tungsten-Titanium Sputtering Target: Applied in thin-film deposition processes for semiconductor manufacturing.
Related reading: Everything You Want To Know About The Most Refractory Metal Tungsten
Preparation of High Purity Tungsten Powder
The preparation methods for high purity tungsten powder are primarily categorized into powder metallurgy, melting, and chemical vapor deposition.
- Powder Metallurgy:
Powder metallurgy involves forming tungsten powder into desired shapes and heating it to a temperature below its melting point. This process, known as sintering, causes material migration and densification, resulting in tungsten billets or simple-shaped tungsten products. Powder metallurgy is advantageous for producing complex shapes with high purity and uniformity.
- Melting Method:
The melting method heats tungsten raw materials above their melting point to form a liquid phase. Impurities are removed during this process, and the material is subsequently cooled and solidified to achieve densification. Various techniques are used in this method:
– Vacuum Consumable Arc Melting: Involves melting tungsten in a vacuum using an electric arc, ensuring minimal contamination.
– Electron Beam Melting: Utilizes a focused beam of electrons to melt tungsten, allowing precise control over the melting process.
– Ion Beam Melting: Employs ion beams to achieve melting, providing high purity and refined grain structures.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD):
CVD is a process where tungsten compound gases, typically tungsten hexafluoride (WF6), are used as the tungsten source. The tungsten compound is reduced by hydrogen (H2) at a specific temperature, depositing tungsten onto a substrate. After deposition, the substrate is removed to yield dense tungsten blanks or finished products. CVD is ideal for producing ultra-pure tungsten with exceptional uniformity and density.
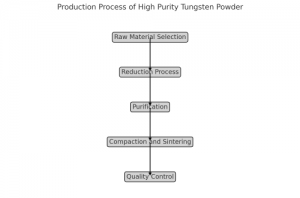
Production Process of High Purity Tungsten Powder
The production of high purity tungsten powder involves several key steps:
- Raw Material Selection: Only high-quality tungsten ore or compounds are used to ensure the initial purity.
- Reduction Process: Tungsten oxide is reduced to tungsten powder using hydrogen in a controlled environment.
- Purification: The powder undergoes multiple purification stages to remove impurities and achieve the desired purity level.
- Compaction and Sintering: The powder is compacted into the desired shape and sintered to enhance density and mechanical properties.
- Quality Control: Rigorous testing and analysis are performed to ensure the final product meets the specified purity standards.
Uses of High Purity Tungsten Powder
High purity tungsten powder is integral to various high-tech and industrial applications due to its exceptional properties:
- High-Temperature Resistant Devices:
High purity tungsten powder is used to produce devices that operate in extreme temperatures, offering superior material properties and extended service life.
- Precision Alloy Casting:
It is added to pure tungsten elements in precision alloy casting to enhance the mechanical and thermal properties of the final product.
- Electronics Industry:
– Resistance Layers and Diffusion Barriers: High purity tungsten and its silicides are used in ultra-large scale integrated circuits (ULSICs) as resistance layers and diffusion barriers, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
– Gate Materials and Connection Materials: Tungsten is employed in metal oxide semiconductor transistors as gate materials and connection materials due to its high resistance to electron migration and stability at high temperatures.
– Sputtered Films: Ultra-pure tungsten (5N or 6N) is often used as a gate, connection, and barrier metal in the electronics industry in the form of sputtered films, providing excellent resistance to electron migration and forming stable silicides.
- Ultra-High Purity Applications:
Ultra-high purity tungsten and its composite materials, such as tungsten-silicon or tungsten-titanium, are made into high-purity sputtering targets. These targets are used to create thin films on substrates or other thin film layers, which are crucial in ULSICs for resistance layers, diffusion barrier layers, and gate materials.
Conclusion
In summary, high purity tungsten powder, with its remarkable purity and exceptional properties, plays a critical role in advanced industrial and technological applications. Its versatility and performance make it indispensable in the production of high-temperature devices, precision alloys, and cutting-edge electronic components. For more details, please check Advanced Refractory Metals (ARM).



